- Benchmark tests revealed that Willow completed a task in under five minutes that would have taken a traditional supercomputer ten septillion years to accomplish.
- Quantum technology is built on principles of quantum mechanics like superposition, entanglement, and quantum error correction, which provide it with a distinct advantage over classical computing.
- India’s National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications (NM-QTA), launched in 2020 with a ₹8,000 crore budget, is driving the development of quantum infrastructure through partnerships and indigenous advancements.
- Nations like the U.S., China, and Russia are integrating quantum innovations into their defence systems, signalling the strategic importance of quantum technology in securing a competitive edge.
The Willow Quantum Chip, developed by Google, represents one of the most significant advancements in computational power in the history of quantum computing. Unlike conventional computers, it employs quantum physics principles to perform calculations at unprecedented speeds and efficiencies. By harnessing the principles of entanglement and superposition, the chip can carry out multiple calculations simultaneously, which is set to revolutionize industries such as medicine development, cryptography, artificial intelligence, and more.
The Willow Quantum Chip’s Operation
At the heart of the Willow Quantum Chip are superconducting qubits, which leverage superposition to maintain multiple states simultaneously. This allows the chip to perform parallel computations, significantly reducing the time required to process a multitude of possibilities compared to traditional computers. The principle of entanglement, where the state of one qubit affects another even when separated, further enhances its computational efficiency.
One of the major challenges in quantum computing is the instability of qubits, which leads to errors. To overcome this, Google designed the Willow chip to incorporate real-time error correction, ensuring precise computations during processing. Benchmark tests revealed that Willow completed a task in under five minutes that would have taken a traditional supercomputer ten septillion years to accomplish. The chip’s superior capabilities were further validated by its success in the random circuit sampling test.
Key Features of the Willow Quantum Chip
Willow is equipped with 105 superconducting qubits, enabling it to solve progressively more complex problems compared to previous quantum processors. Its key strength lies in its scalability, which involves expanding qubit arrays to handle increased complexity while maintaining high performance. The chip’s scalability, combined with its real-time error correction, ensures it can address intricate problems without compromising reliability.
The Willow Quantum Chip’s capabilities are expected to have a transformative impact across various domains. In drug discovery, it can simulate molecular interactions at high speed, expediting the identification of potential molecules. In artificial intelligence, it has the potential to accelerate machine learning models, reduce training times, and enhance model accuracy. Additionally, the chip’s computational power could eventually crack existing encryption methods, leading to the development of more robust and secure cryptographic systems. These advancements lay the groundwork for massive quantum computing systems that are already proving their practicality in multiple sectors.
Fundamental Ideas in Quantum Technology
Quantum technology is built on principles of quantum mechanics that differ significantly from classical physics. The principle of superposition allows qubits to exist in states of both 0 and 1 simultaneously, enabling quantum computers to perform operations based on multiple outcomes at once. Entanglement enhances computational capability by ensuring that the state of one qubit influences another. Quantum interference improves efficiency by amplifying accurate results and minimizing errors, while quantum tunnelling allows particles to bypass energy barriers, aiding in optimization and problem-solving. Quantum error correction, vital for maintaining qubit stability, ensures the reliability of these sensitive systems. Together, these principles provide quantum systems with a distinct edge over classical computing, offering unparalleled opportunities in encryption, communication, and computation.
The Quantum Race Around the World
The United States is a global leader in quantum research, with companies such as Google, IBM, and Microsoft at the forefront. Government initiatives like the National Quantum Initiative Act have laid a strong foundation for advancements in AI, cryptography, and quantum computing. This strategic support ensures the U.S. remains a leader in quantum technology applications.
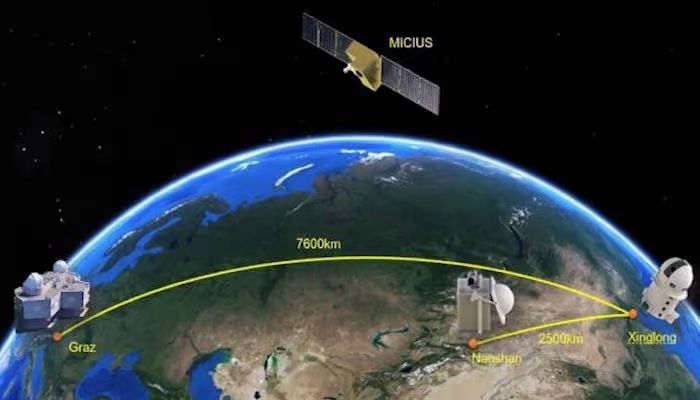
China has emerged as a formidable competitor, with state-led initiatives propelling its progress in quantum communication and cryptography. The Micius satellite, launched in 2016, enabled secure quantum communication between Earth and space, highlighting China’s expertise. The country is also focused on developing quantum hardware and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) systems for secure diplomatic and military communications.
Where Does India Stand?
India is carving out its place in the global quantum race through significant advancements like the collaboration between the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and IIT Delhi under the DRDO Industry Academia–Centre of Excellence (DIA-CoE). Their breakthroughs include demonstrating QKD over a 50 km fibre link and achieving free-space quantum communication over 80 meters. The partnership also achieved hybrid entanglement experiments with a low Quantum Bit Error Rate (QBER) of 6% over 10 meters and prioritized indigenous development of critical components like single-photon sources and detectors.
India’s National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications (NM-QTA), launched in 2020 with a ₹8,000 crore budget, is driving the development of quantum infrastructure. Institutions like the IITs, IISc, ISRO, and DRDO are advancing research, while international collaborations with giants like IBM strengthen India’s capabilities. However, challenges such as a shortage of skilled quantum scientists and engineers, infrastructure gaps, and reliance on imported hardware remain significant hurdles. Limited private sector involvement further slows progress. Overcoming these obstacles is critical for India to remain competitive in the quantum race.
Quantum technologies hold immense potential for transforming defence capabilities. They can enable secure communication through unbreakable encryption, enhance the detection of low-profile targets and stealth aircraft with quantum radar, and improve underwater surveillance, navigation, and identification of biological agents with quantum sensors. While nations like the U.S., China, and Russia are integrating quantum innovations into their defence systems, India must address its challenges to maintain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Google’s Willow Quantum Chip marks a significant milestone in quantum computing, with the potential to revolutionize fields such as artificial intelligence, cryptography, and drug development. The global competition involving the U.S., China, and India underscores the transformative impact of quantum technologies on the future of computing, communication, and defence. Willow demonstrates the practical application of quantum computing to solve problems beyond the reach of classical methods, paving the way for unprecedented technological advancements across industries.
References:
- https://blog.google/technology/research/google-willow-quantum-chip
- Jagran Josh. (n.d.). What is Google Willow Quantum Chip? Faster than a supercomputer. https://www.jagranjosh.com
- Google’s next-gen quantum chip cracks 10-septillion-year computation in minutes. https://www.capacitymedia.com Capacity Media. (2023).
- Google breaks quantum computing record with Willow chip. Retrieved from https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com Times of India. (2023)
- Google’s Quantum Leap: How the Willow Chip Can Revolutionise AI? https://yourstory.com YourStory. (2023).
- https://thequantuminsider.com/2024/10/16/russian-led-research-team-report-qrates-quantum-key-distribution-system-is-ready-for-certification/
Piyush Anand is a Biotechnology Engineering student at Chandigarh University. His primary interest lies in International Affairs, Defence and Strategy. Views expressed are the author’s own.
