
- Vision for Modernization: MBS’s reforms aim to diversify Saudi Arabia’s economy, modernize society, and reduce dependence on oil.
- Geopolitical Strategy: He balances strong ties with the U.S. while fostering relationships with BRICS nations and promoting peace in the region.
- Cultural Reforms: By embracing sports, entertainment, and women’s empowerment, MBS is transforming Saudi Arabia into a progressive nation while addressing internal conservatism.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, once a strict absolute monarchy where even walking freely in open areas was challenging, has undergone a massive transformation. It is now the 17th largest economy in terms of GDP and is emerging as one of the most developed countries in the region, alongside the UAE. In a society where it was once difficult for women to step outside their homes, Saudi Arabia now stands at a pivotal point. Women enjoy newfound freedoms, such as attending music concerts and football stadiums, driving vehicles, and accessing multiple opportunities. These changes reflect the country’s efforts to become a truly open and inclusive society.
In contrast to Saudi Arabia, countries like Yemen to the south, the ongoing confusion surrounding Palestine, and nations like Iraq, Syria, and Lebanon remain some of the most volatile areas in the world. Despite this, Saudi Arabia continues to thrive. A key figure behind this transformation is Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, the newly appointed Prime Minister. He is a leader committed to the mission of modernizing Saudi Arabia, not only in terms of economic growth but also through changes in policies, foreign relations, and governance. Mohammed bin Salman is not shying away from making bold changes, which has raised many eyebrows and left analysts wondering what his next move might be.
The pragmatism of Prime Minister Mohammed bin Salman stems from necessity, driven by regional circumstances. Since the second half of the 20th century, West Asia has witnessed continuous conflict, resulting in the loss of thousands of lives and forcing millions to migrate across the globe. Mohammed bin Salman recognizes that prolonged conflicts could deprive Saudi Arabia of valuable opportunities. He understands that war comes at the cost of human lives and that the country’s limited resources cannot sustain endless warfare.
Another key reason for the changes is his pragmatic approach to the Saudi economy. The country’s economy has traditionally relied on non-renewable resources, particularly fossil fuels, but these are finite. As a result, Saudi Arabia needs to diversify its economy, ensuring it’s not solely dependent on fossil fuels. Significant investments are being made in industries beyond oil, such as renewable energy, job creation, and boosting the tertiary sector. Infrastructure development and diversifying the economy are crucial to ensuring Saudi Arabia’s economic future is not limited to one industry.
One pragmatic aspect of Mohammed bin Salman’s foreign policy is his balanced approach to Islamic Brotherhood principles. Before October 7, 2023, he announced Saudi Arabia’s status under the Abraham Accords. While Saudi Arabia has not fully aligned with Israel, it has refrained from open hostility, recognizing that the Palestinian issue costs the kingdom more than it gains. Saudi Arabia understands the importance of opportunities for peace and progress in engaging with Israel, given the region’s changing dynamics.
Another major geopolitical shift under Mohammed bin Salman is his strategy to maintain Saudi Arabia as the largest defence partner of the United States, purchasing billions of dollars in weapons, while simultaneously resisting complete dependence on American interests. Simultaneously, he aims to align with BRICS, advocate for multipolarity, and foster strong relationships with countries like India, China, and Russia.
One of Mohammed bin Salman’s key challenges has been managing Saudi Arabia’s relationship with Iran. Given Iran’s regional dominance through proxies and its attempts to expand its influence, the situation has often provided third countries, such as the United States, with opportunities for increased involvement in the region. To counter this, Mohammed bin Salman has sought to improve relations with Iran, aiming to reduce tensions and minimize external interference. However, the conflict in Yemen remains a pressing issue. For the past decade, Saudi Arabia has been engaged in efforts to neutralize Iranian-backed Houthi rebels, who have posed a significant challenge to regional stability.
An interesting aspect of Mohammed bin Salman’s approach is his stance on the concept of the Islamic Brotherhood. Historically, the concept has driven Islamic movements, and Saudi Arabia has long been seen as a leader in Islamic missions. However, the notion of the Islamic Brotherhood, particularly through organizations like the Muslim Brotherhood, has often been a source of tension in the region. For instance, the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) has had a strained relationship with India, frequently criticizing the country on various issues.
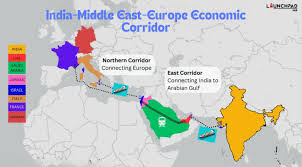
Despite these tensions, Mohammed bin Salman has fostered strong economic and political ties with India. Both countries have moved beyond misunderstandings to develop mutual cooperation. A notable example is the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor agreement, signed during the 2023 G20 Summit in India.
Saudi Arabian society is undergoing a significant transition, with initiatives like bringing top football leagues to the country and making the Saudi Pro League one of the most competitive, along with organizing major music concerts. Mohammed bin Salman has understood society’s needs and is striving to transform it into a developing and prosperous nation. However, in a country like Saudi Arabia, where conservatism still prevails in certain segments of the population, it will be interesting to see how far these reforms can go.
References:
Aayush Pal is a freelance writer on contemporary geopolitical developments. The views expressed in his work are entirely his own.
