
OpenAI has released ChatGPT, a new dialogue language model (LM) based on the GPT-3.5 family series (trained on text and code) and similar to InstructGPT (aligned with reinforcement learning through human feedback). The company set up an online demo which has gone viral among users and reached its first 1 million user accounts in just 5 days! In comparison, it took Netflix 41 months, Facebook 10 months, and Instagram 2.5 months to reach 1 million user accounts.
ChatGPT is a chatbot that can “answer follow-up questions, admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests.” ChatGPT is, by far, the best chatbot in the world. It can write essays and poetry. It can find great prompts for AI art models. It can roleplay. It can write code, find a bug, explain it, solve it, and explain the solution.
The model’s superior abilities and better alignment than other chatbots make it feel more human. Like all other LMs (e.g. GPTs, Galactica, LaMDA) it makes things up, can generate hurtful completions, and produce misinformation.
What is a Chatbot?
A chatbot can be defined as a developed program capable of having a discussion/conversation with a human. Any user might, for example, ask the bot a question or make a statement, and the bot would answer or perform an action as necessary. A chatbot communicates similarly to instant messaging.
A chatbot is a software that simulates human conversations. It enables communication between a human and a machine, which can take the form of messages or voice commands. A chatbot is designed to work without the assistance of a human operator. AI chatbot responds to questions posed in natural language as if it were a real person. It responds using a combination of pre-programmed scripts and machine learning algorithms.
When asked a question, the chatbot will answer using the knowledge database that is currently available to it. If the conversation introduces a concept it isn’t programmed to understand; it will pass it to a human operator. It will learn from that interaction as well as future interactions in either case. As a result, the scope and importance of the chatbot will gradually expand.
How do Chatbots Work?
Bots are made for a specific reason. A store would most likely want chatbot services that assist you in placing an order, while a telecom company will want to create a bot that can address customer service questions.
There are two categories of chatbots: one that works by following a series of rules, and another that uses artificial intelligence.
1. Rule-based chatbots
A rule-based bot can only comprehend a limited range of choices that it has been programmed with. Predefined rules define the course of the bot’s conversation. Rule-based chatbots are easier to build as they use a simple true-false algorithm to understand user queries and provide relevant answers. Rules-based chatbot software performs pre-programmed behaviours based on “playbooks” you create on the user interface’s backend module. Like a digital assistant, rules-based chatbot technology can behave in a certain way based on click activities and simple event triggers like a “yes” or a “no” input. It may also detect a specific keyword or combination of phrases (but only when there is an exact match).
For instance, you could program a rules-based chatbot to answer not only if someone chooses “black” or “white,” but also if they say “I want a black item” – the chatbot’s backend module will match the term black with a preconfigured rule.
2. AI-based chatbots
This bot is equipped with an artificial brain, also known as artificial intelligence. It is trained using machine-learning algorithms and can understand open-ended queries. Not only does it comprehend orders, but it also understands the language. As the bot learns from the interactions it has with users, it continues to improve. The AI chatbot identifies the language, context, and intent, which then reacts accordingly. Artificial intelligence chatbots employ AI and natural language processing (NLP) technology to recognize sentence structure, interpret knowledge, and improve their ability to answer questions.
Instead of relying on a pre-programmed response, AI chatbots first determine what the customer or user is saying. Then, once they have figured out what the user is looking for, the chatbot provides an answer that it believes is correct based on the available data. The machine learns the “right” response over time by analyzing correct and erroneous responses.
With AI-driven decision-making mechanisms, a chatbot can be extremely effective, provided they have a thorough understanding of your organization, its customers, and its context. This functionality is primarily used by large enterprises like e-commerce and other high-volume businesses that demand scale.
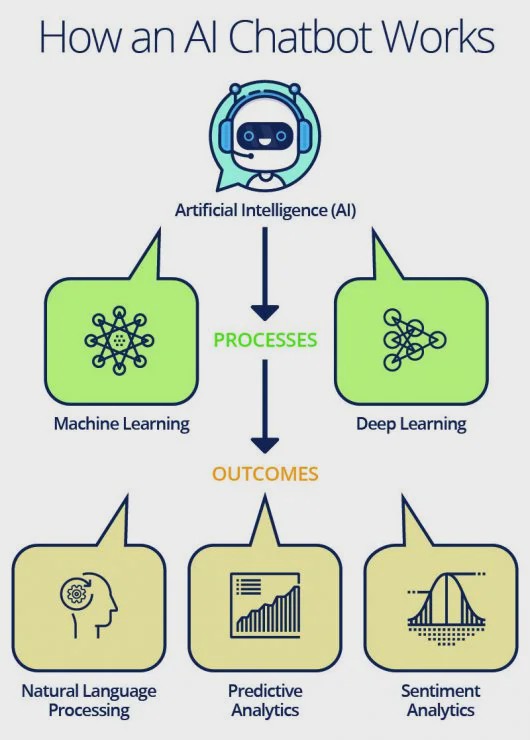
How are Chatbots Trained?
Training a chatbot occurs at a considerably faster and larger scale than human education. While normal customer service representatives are given manual instruction which they must be thorough with, a customer support chatbot is nourished with a large number of conversation logs, and from those logs, the chatbot can understand what type of questions needs, and what kind of answers.
There are three classification models that chatbots adapt to work:
1. Pattern Matchers
Bots use pattern matching to classify the text and produce a suitable response for the customers. A standard structure of these patterns is “Artificial Intelligence Markup Language” (AIML).
A simple pattern-matching example:
The machine then gives an output:
Human: Do you know who Abraham Lincoln is?
Robot: Abraham Lincoln was the US President during the American civil war.
The chatbot knows the answer only because his or her name is in the associated pattern. Similarly, chatbots respond to anything relating to the associated patterns. But it can not go beyond the related pattern. Algorithms can help with an advanced level of work.
2. Algorithms
A unique pattern must be available in the database to provide a suitable response for each kind of question. A hierarchy is created with lots of combinations of patterns. Algorithms are used to reduce the number of classifiers and create a more manageable structure.
Computer scientists call it a “Reductionist” approach- to give a simplified solution; it reduces the problem.
Multinational Naive Bayes is the best example of the algorithm for NLP and text classification. For instance, let’s look at the set of sentences that belong to a particular class. With new input sentences, each word is counted for its occurrence and is accounted for its commonality. Then, each class is assigned a score. The highest-scored class is the most likely to be associated with the input sentence.
Example of Sample Training Set:
Class: Greetings
“How are you doing?”
“Good morning”
“Hi, there!”
Sample Input Sentence Classification:
Input: “Hello, good morning.”
Term: “Hello” (no matches)
Term: “Good” (class: Greetings)
Term: “morning” (class: Greetings)
Classification: Greetings (score=2)
With the help of an equation, word matches are found for the given sample sentences for each class. The classification score identifies the class with the highest term matches, but it also has some limitations. The score signifies which intent is most likely for the sentence but does not guarantee it is the perfect match. The highest score only provides the relativity base.
3. Artificial Neural Networks
Neural Networks are a way of calculating the output from the input using weighted connections, which are computed from repeated iterations while training the data. Each step through the training data amends the weights resulting in the output with accuracy.
As discussed earlier here, each sentence is broken down into individual words, and each word is then used as input for the neural networks. The weighted connections are then calculated by different iterations through the training data thousands of times, each time improving the weights to make it accurate.
The trained data of a neural network is a comparable algorithm with more and less code. When there is a comparably small sample, where the training sentences have 200 different words and 20 classes, that would be a matrix of 200×20. But this matrix size increases by n times more gradually and can cause a massive number of errors. In this kind of scenario, the processing speed should be considerably high.
There are multiple variations in neural networks, algorithms as well as patterns matching code. Complexity may also increase in some of the variations. But the fundamental remains the same, and the critical work is that of classification.
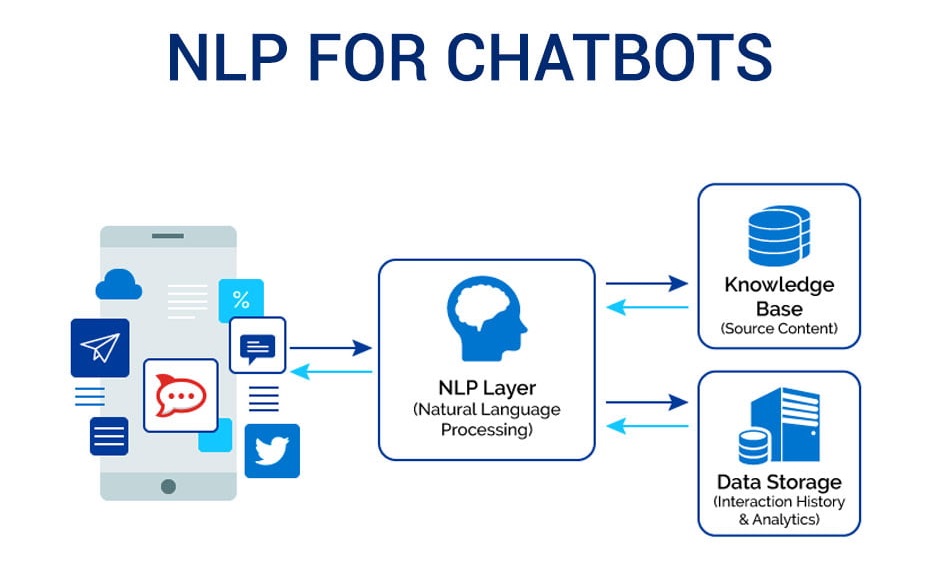
What are the Commercial Benefits of Chatbots?
Chatbots help companies by automating various functions to a large extent. Through chatbots, acquiring new leads and communicating with existing clients becomes much more manageable. Chatbots can ask qualifying questions to the users and generate a lead score, thereby helping the sales team decide whether a lead is worth chasing or not.
Chatbots can help a great deal in customer support by answering questions instantly, which decreases customer service costs for the organization. Chatbots can also transfer complex queries to a human executive through chatbot-to-human handover.
Chatbots can be used to simplify order management and send out notifications. Chatbots are interactive in nature, which facilitates a personalized experience for the customer. You can read more about chatbots in our complete guide on chatbots.
How are chatbots useful?
- Chatbots are becoming increasingly important due to their financial benefits.
- Chatbots provide individual connections to a limitless number of users at scale.
- Chatbots automate routine functions.
- Chatbots make it easy to have excellent customer service and a customized experience
- Chatbots are social, allowing for a two-way dialogue with suggestions.
- Chatbots are very efficient.
