- Cybersecurity Ventures estimates that cybercrime losses across the globe are expected to rise to $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, underscoring the need for effective cybersecurity protection.
- China being unable to wrestle control in the conventional ways turned to cyber warfare advantage where the code of conduct is ill-defined and the damages can be crippling yet not easily attributable.
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups affiliated with Pakistan, such as SideCopy and APT36 (Transparent Tribe), have been increasing their activity targeting Indian government and military institutions.
- India has to increase the scope and scale of the cyber nexus with other advanced countries like the EU, the US, Taiwan and Japan.
Security in cyberspace is now an important issue of concern in just about every field and definitely for all of us. While applying technologies at a faster rate introduces innovation and promising opportunities, it also creates conditions that facilitate advanced cyber threats. Some recent cyber threats, including the Ascension attack and the French State DDoS attack, have been seen as a potential threat to life.
Emerging Cyber Threats
Cyberspace is dynamic, and the hackers are smarter now making them more resilient and dynamic in their approach. Cybersecurity Ventures estimates that cybercrime losses across the globe are expected to rise to $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, underscoring the need for effective cybersecurity protection.
Ransomware Evolution
One notable trend highlighted in the Cybersecurity Ventures review is that ransomware attacks are not limited to merely locking data and demanding a ransom any longer. Contemporary ransomware is about stealing data and threatening its publication, causing disruption and reputational damage.
In a recent attack in May, the Black Basta group that has connections with Russia attacked the largest non-profit Catholic health system in the U. S known as Ascension, causing the clinical operations all through its 140 hospitals to be cut off Electronic Health Records (EHR). This disruption greatly impacted the company’s patient care since they had to temporarily halt some non-emergency elective procedures in their facilities.
Supply Chain Attacks
Besides ransomware, another major cybersecurity risk category is supply chains. These attacks aim at the weaknesses and blind spots in a supply chain network using third parties, to ensure that the entire supply chain is secured.
AI-Driven Cybercrime
Additionally, AI is also used by cybercriminals to increase their sophistication in terms of attack methods. Malware can be self-evolving and AI is also used in developing deep fake content for impersonations in social engineering attacks. Consider the following examples of AI-powered attacks taking over the headlines:
DeepLocker: Self-contained AI malware created by IBM scientists, which only becomes activated when it gets to a specific location.
Deepfakes: In the same year, hackers adopted AI in an email impersonation scam where the company’s employee was defrauded and made to release large sums of money.
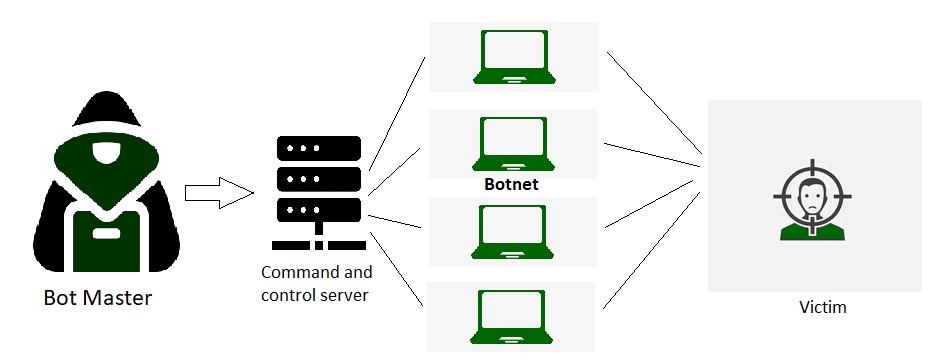
DDoS Attacks: Other critical threats include Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks by heavily taxing a target’s network or website through an avalanche of traffic making it inaccessible.
In March 2024, more than 300 web domains and 177,000 IP addresses linked to the French government were affected by a big DDoS attack. The attack was said to have been conducted by Anonymous Sudan, but it is believed to have been an attempt to support Russia as some of the targeted sites are related to public services.
The Role of AI in Cybersecurity Defense
Advanced AI has facilitated cyber attackers to grow in range but also has offered a very effective weapon to deal with cyber threats. The AI features for threat detection and threat response have become indispensable tools in cybersecurity. Artificial intelligence, through the use of computing models, processes the available data with the view of making decisions on whether a cyber-attack is underway.
AI networks are used to scan the latter for ‘abnormal’ behaviour and alert security forces if they perceive threats. Sophisticated AI-enabled workbenches supplement security analysts in the investigation and management of these threats. Further, AI solutions analyze the behaviours of the users to fight insider threats, and this investigation involves the use of machine learning algorithms to find odd behaviours, which makes the security posture stronger.
The threat is manifold and organizations find it hard to protect client data, especially in today’s world where these threats are becoming more and more evolved. With AI threat detection technology, they can detect threats and neutralise them independently, which will reduce their vulnerability and increase trust from clients.
Strategies for Developing a Strong Cybersecurity Framework
To address such threats, organisations and countries have to work hard and ensure that a solid cybersecurity system is put in place. A zero-trust approach also mediates every access request, irrespective of the source, to eliminate privileged access misuse. Some of the key components are multi-factor authentication, reducing the level of access granted to an individual and segmentation of the network.
However, the protection mechanisms need to be smarter and more proactive with tools and techniques that can identify threats and prevent them in real-time. SIEM systems, in conjunction with advanced analytics, offer a versatile approach to watch over the underlying network activity and raise alarms when specific threats are detected.
Also, we cannot leave out the discussion of human factors in cybersecurity as an important factor to consider. Prevention of human-related errors is also necessary due to the high risk of errors made by the employees. Ongoing training sessions can ensure that employees are knowledgeable enough to prevent such threats for instance phishing attacks thus fostering a security-conscious organization and eradicating the success of such attacks.
Cyber Warfare and Global Security: New Directions
With an increase in cyber warfare, there are issues to global security which must be addressed. The threats that are present on the indirect level and directly aim at challenging the security apparatus and cyber security infrastructure of the nation are tangible. Using cyber warfare, either by state actors or cyber spies, disruptive activities can cause instability in nations and affect important infrastructures.
Chinese Cyber Threats to India
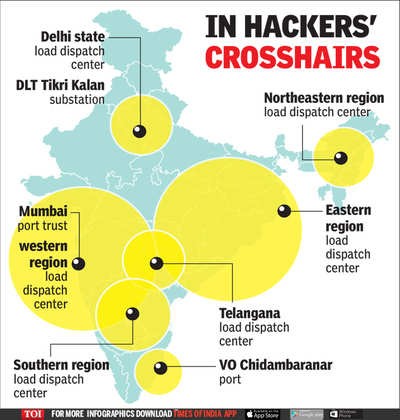
China has actively attacked India through unauthorized cyber operations that target the population, key facilities, and important segments of the economy. These attacks seek to disrupt operations, obtain confidential information and gain an edge over competitors in India. Some of the severest attacks witnessed after the Ladakh confrontations between Indian and Chinese troops in June 2019, were the Mumbai grid attack in January 2021 and the ransomware attack on AIIMS Delhi in 2022.
Ladakh Confrontations
June 2019 saw physical confrontations between Indian and Chinese troops, at the Line of Actual Control in Ladakh. These confrontations showed that China which is relatively inexperienced in high-altitude warfare could not effectively face the military might of India. Unable to counter India in conventional ways, China has turned to cyber warfare where the code of conduct is ill-defined and the damages can be crippling yet not easily attributable.
Cyber Attacks on Critical Infrastructure
The most famous instance of cyberattack emanating from China was detected in December 2020, when the SSL VPN devices of the Indian government were targeted. SSL VPNs enable a user to access his organization’s network from any point of the public internet connection, a crucial factor for government officials dealing with sensitive information. These specific attacks were blamed on the Chinese cyber espionage group APT-41 also referred to as Double Dragon, which is believed to be linked to the Chinese State machinery.
The Mumbai Power Grid Attack
January 2021 saw another major power disruption by hackers affecting the Mumbai power grid leading to blackouts in some areas of the city. The hackers were said to be acting at the behest of China, which was seeking revenge for the Galwan fiasco and other battles. The hack caused power outages in one of the largest metropolitan cities of India and gave a glimpse of the possible repercussions of cyberspace warfare.
Implementing the Economic Strategy for the Health Sector during the Pandemic
As the COVID-19 Delta wave created a surge in India, China further increased its cyberattacks, particularly in the healthcare and logistics sectors. These attacks intensified an already precarious state by causing system collapses and oxygen delivery hitches. It was confirmed that the hacking group APT-10, also known as Stone Panda, attacked Bharat Biotech and the Serum Institute of India (SII) to steal vaccine data and achieve a competitive advantage.
Attack on AIIMS Delhi and Beyond
In November 2022, one of the most reputed medical institutions in India, AIIMS Delhi, was attacked by a ransomware virus, leaking the patients’ data, including the VIPs. This attack exposed the weaknesses of the cybersecurity system in India and brought home the importance of strong cybersecurity systems.
Cyber Threats from Pakistan
Targeting Government and Military
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups affiliated with Pakistan, such as SideCopy and APT36 (Transparent Tribe), have been increasing their activity targeting Indian government and military institutions. Not only are these groups conducting potentially damaging cyberattacks on high-profile entities, but it is also engaging in spear-phishing campaigns like Operation RusticWeb and FlightNight, more risky during an election period.
A new analytical report shows the growth of cyber-attacks from these Pakistan-associated APTs. In the first quarter of the year 2024, there were over 2,900 disruptive attacks comprising individual DDoS attacks, website defacements, and database leaks by more than 85 Telegram-based hacktivist groups.
Espionage Campaigns
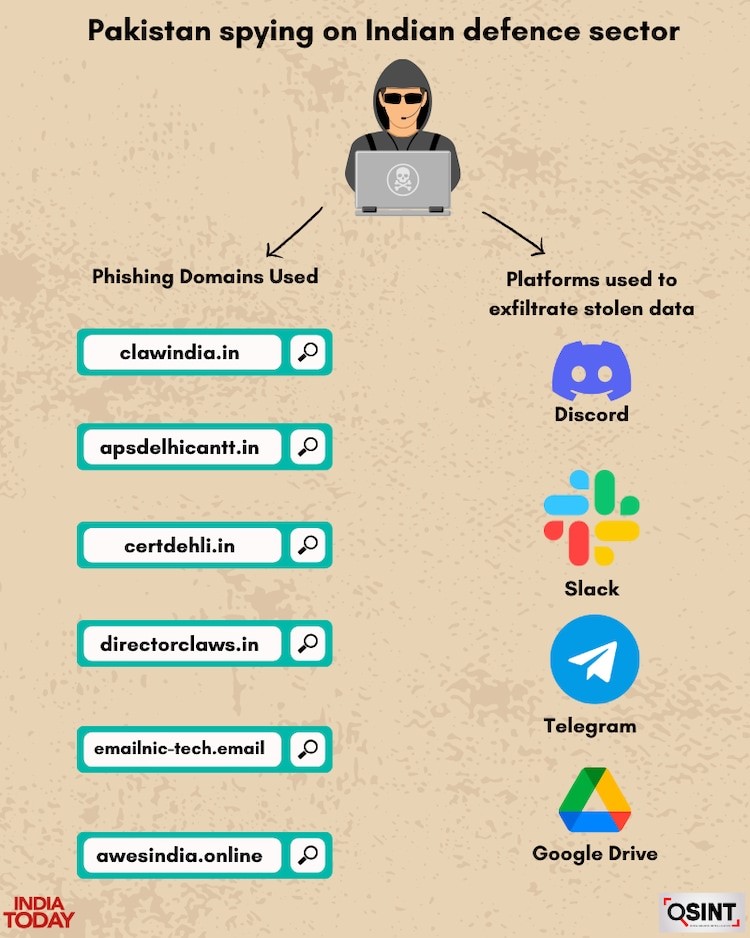
Pakistani hackers have targeted ‘Make in India’ Defense Programs. According to BlackBerry Research & Intelligence Team, between September 2023 and April 2024 Pakistan-affiliated ‘Transparent Tribe’ (APT36) launched a cyber-espionage campaign against the Indian defence establishment involving employees of companies under the Ministry of Defence’s Department of Defence Production. This campaign was to target organizations well known to be run by the military and private partnerships.
Through phishing emails, the group intended to deploy malware that would compromise systems operating on Linux and steal sensitive information from “one of the largest aerospace and defence companies in Asia,” “an Indian state-owned aerospace and defence electronics company,” and “Asia’s second-largest manufacturer of earth-moving equipment, which plays a key role in the country’s Integrated Guided Missile Development Project by supplying ground support vehicles”. The companies most likely targeted are Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), and Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML), all headquartered in Bengaluru.
Despite their cyber capabilities, it is ironic that Pakistan uses its technology to target India instead of using its expertise to address its own country’s economic struggles and foster growth.
International Concerns and the Indian Perspective
Cyber warfare can have a tremendous impact on the security of any country. They are a threat to the stability of countries such as India in the sense that as cybercriminals grow in capability they become a much more potent force. The penetration of India’s vital infrastructure such as power stations, banks, hospitals as well as telecom networks suggests that future warfare could undermine the public’s confidence in their government and the basic services required to sustain their lives.
These cyber threats are real but require a layered response that encompasses soft and hard measures on the part of India. Measures that could help to enhance cybersecurity include: building up the legal framework to protect cyberspace around the world, enhancing cooperation with federal bodies of executive power and other states as well and intensifying research of cyber defence measures. Also, ensuring international cooperation that prevents cyber threats and developing a strong legal regime for countering cyber warfare are crucial factors in maintaining the security of the state.
Securing India’s Digital Future
The perception of cyber threats in India lies far away from the reality. There are vast opportunities that can be explored and developed to improve cybersecurity in the country. Some areas that can be considered are: Implementing and establishing capacity-building and confidence-building measures; increasing the scope and scale of the cyber nexus between India and other advanced countries like the EU, US, Taiwan and Japan; establishing new norms for data management and data sharing; a targeted and proportionate deployment and regulation of AI tools to the maximum extent possible and in a secure manner; the using of international systems for the advancement of cyber security.
India and Japan held a crucial annual summit in 2023, which modelled a good opportunity for cooperation in the cyber realm. Evaluating the state of affairs in cybersecurity and the development of advanced systems including 5G, the dialogue creates opportunities for cooperation. One of the most recent areas of cooperation to highlight is the potential for enhancing relations within Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) to draw upon and build upon shared skills and innovations. Additionally, India has made significant progress in a technological frontier including Artificial Intelligence, telecommunications, and the emerging technology domain, making it one of the leaders across the world.
The proposed Joint Indo-US Quantum Coordination Mechanism presents a unique opportunity for cooperation with the United States. Through technology exchange, India can build its cybersecurity knowledge base by collaborating in quantum, AI and next-generation wireless research. The signed implementing arrangement makes allowance for not only research but also the commercialization and inclusive public-private partnership. This is a perfect opportunity for India as the collaboration can enhance the country’s cybersecurity system by incorporating advanced products and expertise from the cooperation.
Last but not least, the United States, India and Taiwan have formed crucial partnerships in the field of cybersecurity making them a significant workshop of the Global Cooperation and Training Framework (GCTF) in December 2023. This event implicates a strong intention and significant engagement of international cooperation in addressing cybersecurity threats: the event was co-hosted by US Ambassador to India Eric Garcetti, Representative of Taiwan Baushuan Ger and former National Cyber Security Coordinator of India Lt Gen Rajesh Pant. Garcetti stressed that by focusing on technology advancement that aimed to increase cybersecurity, creativity had been unlocked and it was time to take a ‘more collaborative’ approach.
Conclusion
Cyber security is a dynamic area of practice as new threats are constantly emerging as well as becoming increasingly ingrained in human activities. That is a statement that has gained credence especially now in the globalized world where cybersecurity is of paramount importance. By adopting high-tech measures, promoting global cooperation, and paying attention to cybersecurity education, nations
References:
- https://www.darkreading.com/cyberattacks-data-breaches/cyber-warfare-understanding-new-frontiers-in-global-conflicts
- https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2023/02/17/cyber-security-concerns-a-threat-to-indias-national-security
- https://thediplomat.com/2024/01/securing-indias-digital-future-cybersecurity-urgency-and-opportunities
- https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/pakistani-hacker-make-in-india-defence-programs-espionage-osint-2544545-2024-05-27
- https://youtu.be/qgfm9E-JqTk
- https://youtu.be/EzGuWLdK1Uk
