- Recent naval interceptions in the disputed maritime area, notably involving vessels conducting hydrocarbon prospecting studies, intensified the conflict.
- Guyana vehemently defended its rights in the exclusive economic zone, highlighting the precarious nature of the situation.
- The decision by the Venezuelan government to proceed with a consultative referendum has added a new layer to an already complex geopolitical landscape.
- The impact on India is diverse, notably in light of the recent resumption of oil supplies from Venezuela.
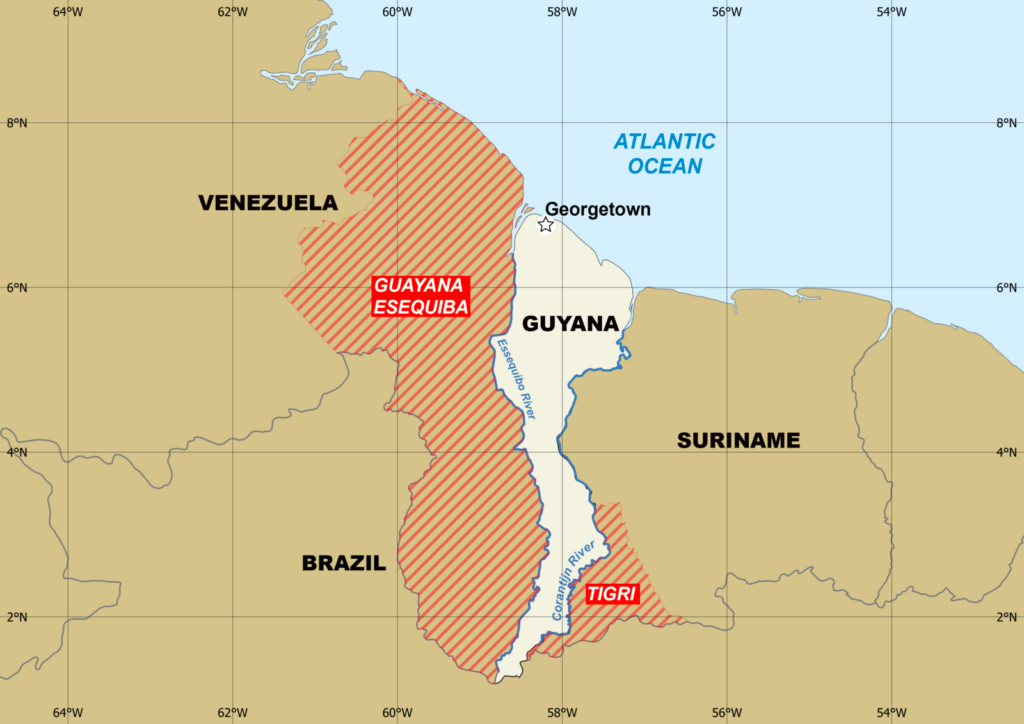
In a significant turn of events, the president of the Venezuelan National Assembly has made a groundbreaking announcement, revealing plans for a consultative referendum to determine the potential annexation of the Essequibo region in Guyana. This revelation has not only stirred tensions but has also placed a spotlight on a longstanding territorial dispute between these South American neighbours. The Essequibo region, spanning over 160,000 km², boasts offshore oil areas with immense potential for exploitation and is home to an estimated population of around 125,000 inhabitants.
Historical Context
Delving into the historical roots of the conflict, the dispute traces back to 1841 when the Venezuelan government contested the Schomburgk Line—a border drawn by a British expedition, granting the United Kingdom control over the mouth of the Orinoco River. Though the UK offered concessions, Venezuela’s dissatisfaction led to appeals for U.S. intervention under the Monroe Doctrine. The late 19th century witnessed attempts at resolution, culminating in the signing of the Treaty of Washington in 1897. However, the matter resurfaced in the 1960s when Venezuela, addressing the United Nations, disavowed previous agreements, setting the stage for ongoing tensions.
Despite sporadic agreements between the two nations over the years, the dispute persisted, eventually landing at the doorstep of the International Court of Justice (ICJ). The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a temporary softening of Venezuelan foreign policy towards Guyana. Nevertheless, in the early 2000s, the discovery of oil in the disputed Stabroek Block reignited hostilities.
Recent naval interceptions in the disputed maritime area, notably involving vessels conducting hydrocarbon prospecting studies, intensified the conflict. Guyana vehemently defended its rights in the exclusive economic zone, highlighting the precarious nature of the situation. The decision by the Venezuelan government to proceed with a consultative referendum has added a new layer to an already complex geopolitical landscape. This move has triggered a massive domestic campaign, engaging 20 million eligible voters through electronic ballot boxes distributed across 28,000 tables in 15,000 voting centres in Venezuela.
U.S. Involvement
The United States, traditionally asserting its influence in Latin America, sought to capitalize on the Venezuela-Guyana dispute. Using Guyana’s security as a pretext, the U.S. has been actively pursuing control over Guyana’s military base since last year. The strategic goal is to secure access to the oil reserves to meet its energy demands, thereby reinforcing its regional dominance.
Venezuelan Strategy
On the other side, Venezuela, under the leadership of President Maduro, views the Essenquibo as not only an opportunity to tap into its oil wealth but also as a strategic move to resist American influence in the region. In preparation for a potential invasion, Venezuela aims to establish dominance and limit U.S. presence, further complicating the delicate balance in Northern Latin America.
Guyana’s Dilemma
Caught in the crossfire, Guyana finds itself in a precarious situation with limited options. In response to the escalating tensions, Guyana is left with no choice but to seek assistance from the United States, highlighting the complex web of alliances and dependencies in the region.
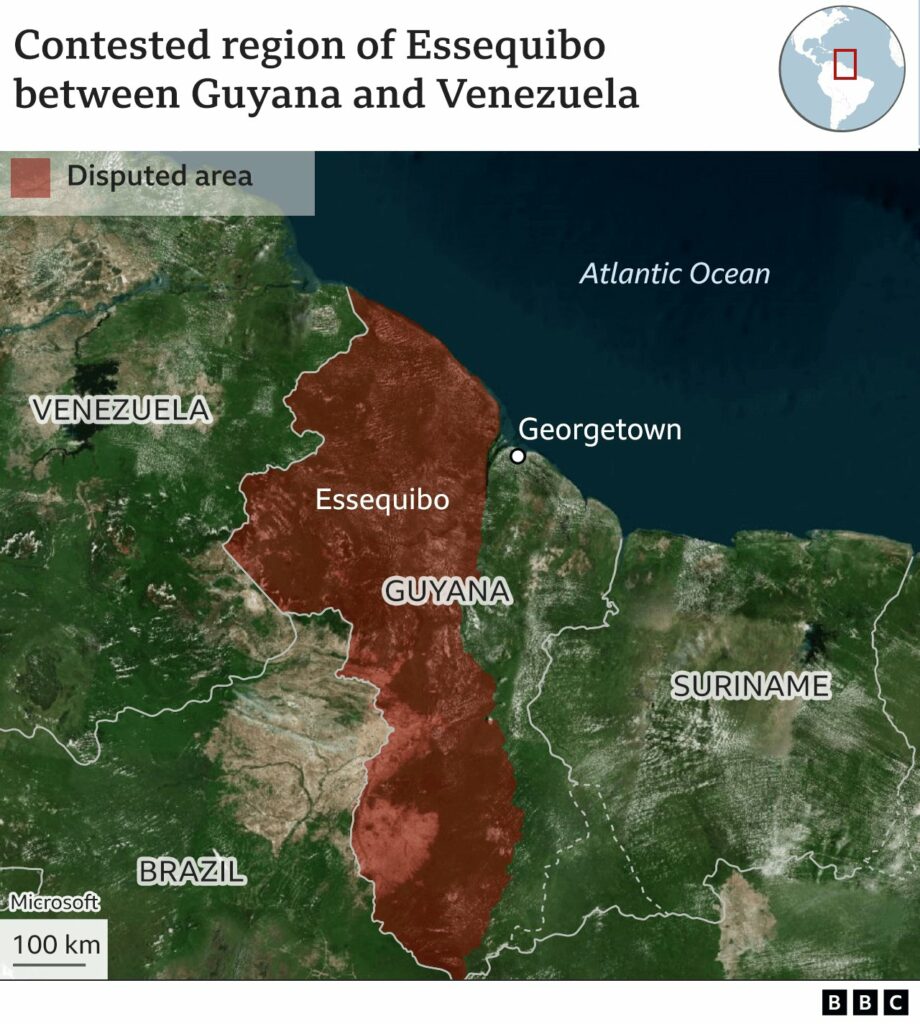
Impact on India and the world
The impact on India is diverse, notably in light of the recent resumption of oil supplies from Venezuela. This development follows Venezuela’s struggle with US sanctions, partially alleviated earlier this year by the Biden administration. The eased sanctions, specifically targeting China’s substantial discounts from Venezuela, have implications for the global oil market.
Against the backdrop of existing global crises, such as the Israel-Hamas war and the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the Venezuela-Guyana conflict introduces additional complexities. These conflicts, with their far-reaching consequences on regional stability, also hold the potential to influence the global economy, food security, and oil security. Given the volatility in global oil prices due to Middle East conflicts and OPEC production cuts, the prospect of conflict in an oil-rich nation like Venezuela adds to the intricate geopolitical landscape.
Alterations in the South American region can raise concerns among major global players, including China and the United States. The multifaceted nature of these developments underscores the need for careful observation and strategic considerations on the part of India, as it navigates the broader implications on energy security and geopolitics.
International Response
The international community has responded with concern. Brazil, in particular, has initiated bilateral talks, especially with Venezuela, in a bid to mediate and prevent the escalation of the conflict. Brazil’s apprehension is rooted in the potential impact on its shared land border with both nations and its interests in an oil prospecting area adjacent to the Guyana plateau.
Regional organizations, including the Caribbean Community (Caricom), the Commonwealth of Nations, and the Organization of American States (OAS), along with the United Nations (UN), have issued statements rejecting the referendum. This comes in the wake of increased military actions along the borders between Venezuela and Guyana.
The historical backdrop of this territorial dispute, once overshadowed by domestic concerns, has now gained international attention. The recent focus on oil reserves has added a new dimension, intensifying regional tensions over resource clashes. As the situation unfolds, it becomes paramount to approach the dispute with a careful diplomatic strategy that respects the sovereign rights of both nations. The hope is for a peaceful resolution that acknowledges the historical intricacies while addressing contemporary geopolitical and economic realities.
(The author is a post-graduate student in International Relations at Kalinga University, Raipur. Views and opinions expressed are the author’s own)
Aayush Pal is a freelance writer on contemporary geopolitical developments. The views expressed in his work are entirely his own.
